Tutorial: Preferential Optimization
What is Preferential Optimization?
Preferential optimization is a method for optimizing hyperparameters, focusing of human preferences, by determining which trial is superior when comparing a pair. It differs from human-in-the-loop optimization utilizing objective form widgets, which relies on absolute evaluations, as it significantly reduces fluctuations in evaluators’ criteria, thus ensuring more consistent results.
In this tutorial, we’ll interactively optimize RGB values to generate a color resembling a “sunset hue”, aligining with the problem setting in this tutorial. Familiarity with the tutorial ob objective form widgets may enhance your understanding.
How to Run Preferential Optimization
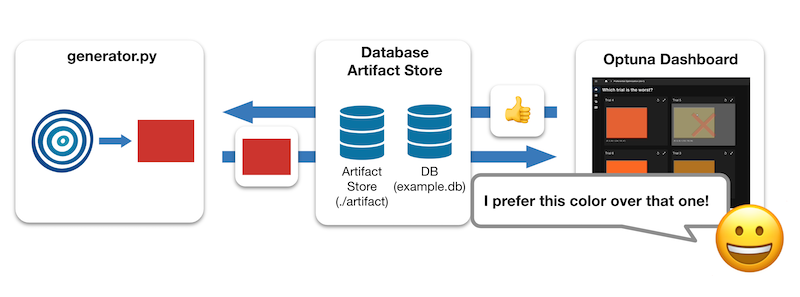
In preferential optimization, two programs run concurrently: generator.py performing parameter sampling and image generation, and the Optuna Dashboard, offering a user interface for human evaluation.
First, ensure the necessary packages are installed by executing the following command in your terminal:
$ pip install "optuna>=3.3.0" "optuna-dashboard[preferential]>=0.13.0b1" pillow
Next, execute the Python script, copied from generator.py.
$ python generator.py
Then, launch Optuna Dashboard in a separate process using the following command.
$ optuna-dashboard sqlite:///example.db --artifact-dir ./artifact
Here, the storage is configured to sqlite:///example.db to retain Optuna’s trial history,
and --artifact-dir ./artifact is specified to store the artifacts (output images).
Listening on http://127.0.0.1:8080/
Hit Ctrl-C to quit.
Upon executing the command, a message like the above will appear. Open http://127.0.0.1:8080/dashboard/ in your browser to view the Optuna Dashboard:
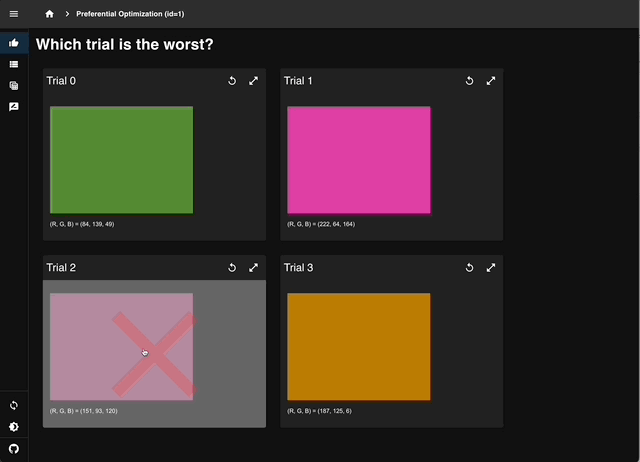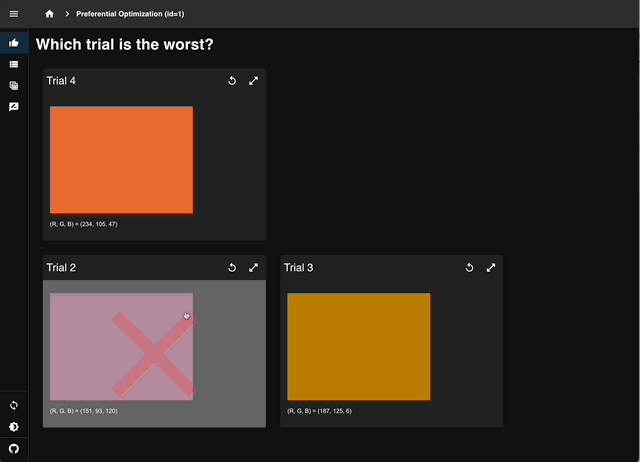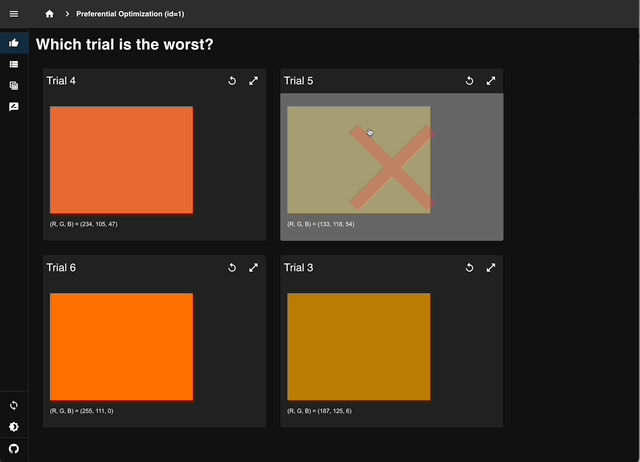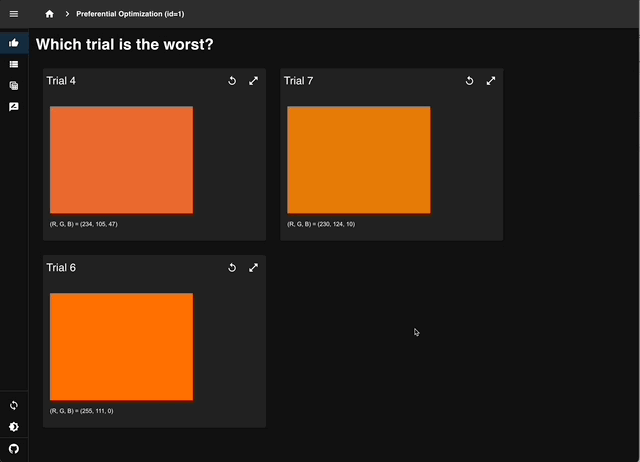
Select the least sunset-like color from four trials to record human preferences.
Script Explanation
First, we specify the SQLite database URL and initialize the artifact store to house the images produced during the trial.
1STORAGE_URL = "sqlite:///example.db"
2artifact_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "artifact")
3artifact_store = FileSystemArtifactStore(base_path=artifact_path)
4os.makedirs(artifact_path, exist_ok=True)
Within the main() function, creating dedicated Study and Sampler objects since preferential optimization relies on the comparison results between trials, lacking absolute evaluation values for each one.
Then, the component to be displayed on the human feedback pages is registered via register_preference_feedback_component().
The generated images are uploaded to the artifact store, and their artifact_id is stored in the trial user attribute (e.g., trial.user_attrs["rgb_image"]),
enabling the Optuna Dashboard to display images on the evaluation feedback page.
1from optuna_dashboard import register_preference_feedback_component
2from optuna_dashboard.preferential import create_study
3from optuna_dashboard.preferential.samplers.gp import PreferentialGPSampler
4
5study = create_study(
6 n_generate=4,
7 study_name="Preferential Optimization",
8 storage=STORAGE_URL,
9 sampler=PreferentialGPSampler(),
10 load_if_exists=True,
11)
12# Change the component, displayed on the human feedback pages.
13# By default (component_type="note"), the Trial's Markdown note is displayed.
14user_attr_key = "rgb_image"
15register_preference_feedback_component(study, "artifact", user_attr_key)
Following this, we create a loop that continuously checks if new trials should be generated, awaiting human evaluation if not.
Within the while loop, new trials are generated if the condition should_generate() returns True.
For each trial, RGB values are sampled, an image is generated with these values, saved temporarily.
Then the image is uploaded to the artifact store, and finally, the artifact_id is stored to the key, which is specified via register_preference_feedback_component().
1while True:
2 # If study.should_generate() returns False, the generator waits for human evaluation.
3 if not study.should_generate():
4 time.sleep(0.1) # Avoid busy-loop
5 continue
6
7 trial = study.ask()
8 # Ask new parameters
9 r = trial.suggest_int("r", 0, 255)
10 g = trial.suggest_int("g", 0, 255)
11 b = trial.suggest_int("b", 0, 255)
12
13 # Generate an image
14 image_path = os.path.join(tmpdir, f"sample-{trial.number}.png")
15 image = Image.new("RGB", (320, 240), color=(r, g, b))
16 image.save(image_path)
17
18 # Upload Artifact and set artifact_id to trial.user_attrs["rgb_image"].
19 artifact_id = upload_artifact(trial, image_path, artifact_store)
20 trial.set_user_attr(user_attr_key, artifact_id)